Structure and Functions of Uterus
Definition
- hollow muscular organ
- one of the internal organs of female reproductive system
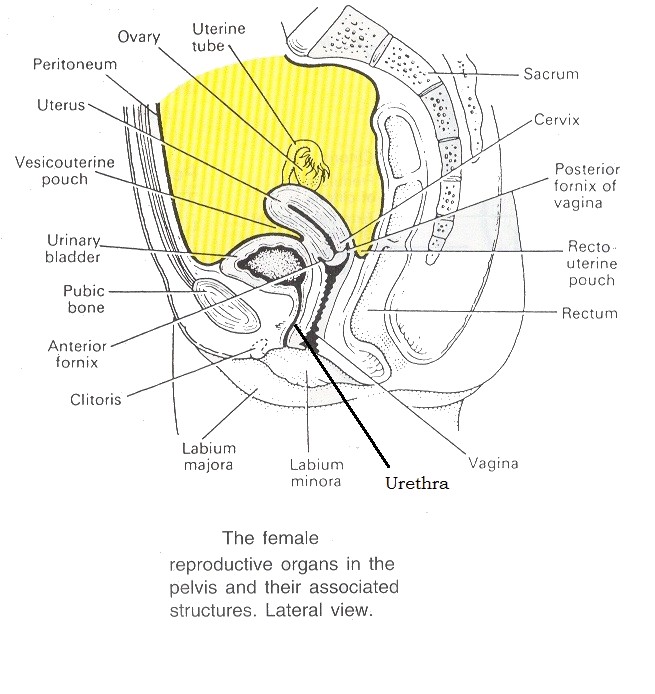
Situation and Position
- in the pelvic cavity
- between urinary bladder and rectum
- anteverted
- anteflexed
- at right angles to the vagina
- anterior surface rests on the urinary bladder
Structure
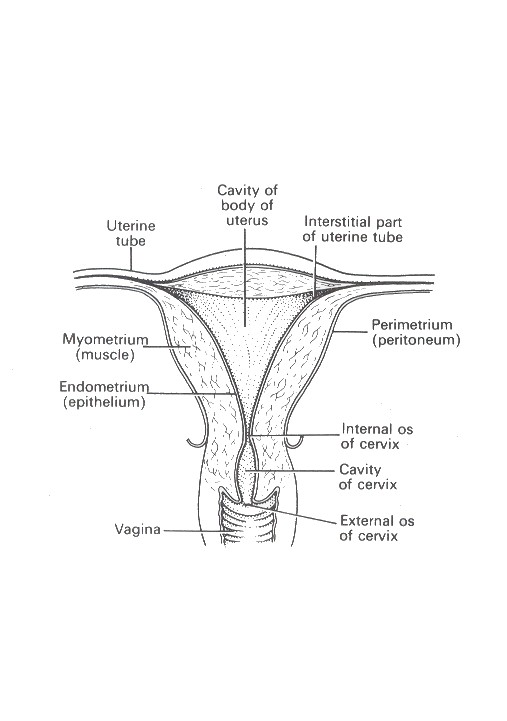
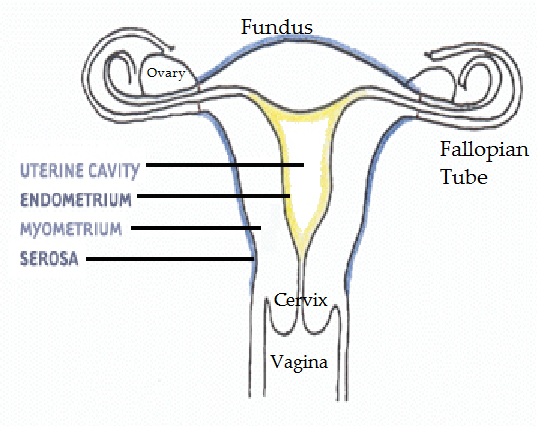
flattened anteroposteriorly
pear shaped
the different parts are : -
1. fundus - dome shaped part
2. body - main part. Narrowest inferiorly at the internal os where it continues with cervix
3. cervix - protrudes through the anterior wall of the vagina, opening into it at the external os.
Wall of the uterus three layers
I. perimetrium
Consists of peritoneum - anteriorly peritoneal covering forms a fold vesicouterine pouch
- posteriorly forms rectouterine pouch
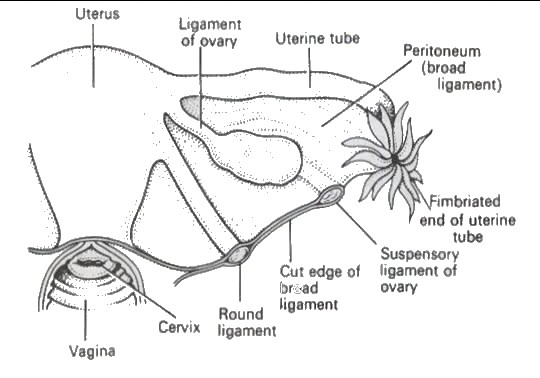
- laterally forms broad ligament
II. Myometrium
thickest layer - smooth muscle fibres - contains a little areolar tissue, blood vessels and nerves
III. Endometrium - columnar epithelium - mucous secreting glands - thickness varies during the monthly menstrual cycle - the upper 2/3 of the cervical mucous membrane;
- the lower 1/3 squamous epithelium continuous with that of the vagina
Blood supply, lymph drainage and nerve supply
- uterine arteries - branches of internal iliac arteries
- venous drainage into internal iliac veins
- lymph drains into aortic lymph nodes and groups of nodes associated with the iliac blood vessels.
- Nerve supply sympathetic from the lumbar outflow - parasympathetic from sacral outflow
Supports of uterus
1. broad ligaments
2. round ligaments
3. uterosacral ligaments
4. transverse cervical ligaments (cardinal ligaments)
5. pubocervical fascia.
Functions
Menstrual cycle
Embeds the fertilized zygote - pregnancy - full term - labour - delivery of the baby.