Ulcerative Colitis
Definition
It is a recurrent ulcerative and inflammatory disease of the mucosal layer of the colon and rectum.
It is a serious disease with systemic complications & high mortality rate
Incidence
Peak - 30 to 50 years of age
Pathophysiology
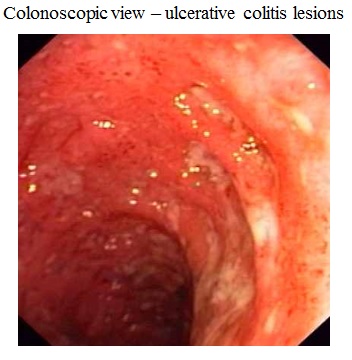
Affects the superficial mucosa of the colon 'multiple ulcerations
Diffuse inflammation, desquamation of the colonic epithelium
Ulcers may bleed
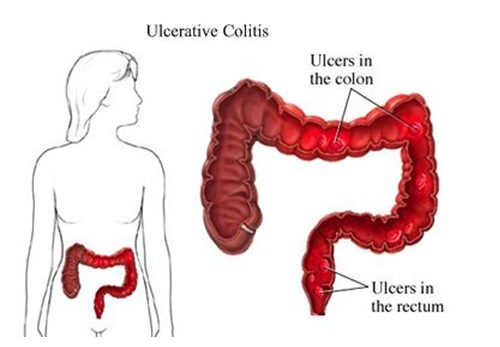
Lesions are continuous
Disease begins in the rectum and may involve the entire colon
The bowel narrows shortens and thickens because of muscular hypertrophy and fat deposits
The inflammation may spread into the muscularis, inhibiting its ability to contract ' toxic megacolon - distension of the colon
Clinical manifestations
Exacerbations and remissions
Anorexia,
fever,
vomiting, Weight loss
Abdominal pain
Urgent need to defaecate
Diarrhoea
Intermittent tenesmus
Passage of 10 - 20 liquid stools a day
Rectal bleeding
dehydration
Rebound tenderness RIF
Skin lesions (erythema nodosum), eye lesions (uveitis), joint abnormalities (arthritis) and liver disease
Hypocalcaemia, anaemia
Investigations
Hb - may be low
TC - raised
ESR - raised
Albumin level - low
Electrolyte imbalance +
Sigmoidoscopy : Mucosal inflammation, friability, exudate and ulcerations
Barium enema : rigid pipe like appearance with no haustrations, thickening of mucosa due to inflammation
Caution to nurses
In acute ulcerative colitis no enema -(especially cathartics) - perforation may occur
If any preparation is necessary at all, give liquid diet for a few days and then a gentle tap water enema on the day of the investigation may be done
Complications
Toxic megacolon
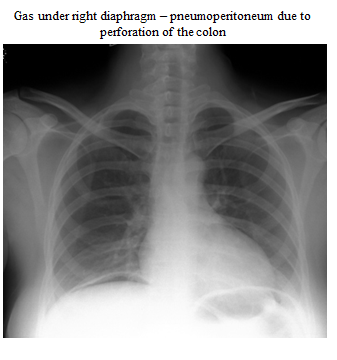
Perforation - high mortality
Bleeding as a result of ulceration
Highly vascular granulation tissue ' pseudo polyps
Management
Medical treatment
Suppress inappropriate immune responses
Reduce inflammation
Provide rest to the diseased bowel
Nutritional therapy
Surgical resection of the colon and ileostomy
Nutritional therapy
Oral fluids
Low residue, high -protein, high calorie diet
Vitamin supplements
Iron replacement
Correction of fluid and electrolyte imbalance by IV fluids
Avoid milk
Avoid cold foods and smoking
Total parental nutrition may be needed
Pharamacologic Therapy
Sedatives
Antidiarrhoeals
Antiperistaltic drugs
Sulphonamides such as sulfasalazine, sulfisoxazole
Antibiotics for infection like abscesses, perforations, peritonitis
Parenteral adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
New topical and oral aminosalicylates (e.g.mesalamine, olsalazine are very effective in treatment).
Immunosuppressants used to reduce the dosage of corticoids and to prevent recurrences.
Surgical Management
Strictureplasty
Resection and anastomosis
Segmental colectomy with anastomosis
Total colectomy and ileostomy