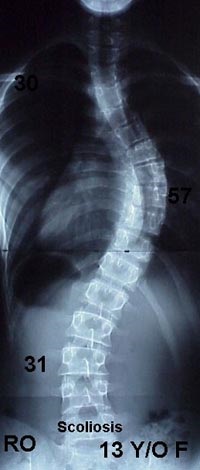
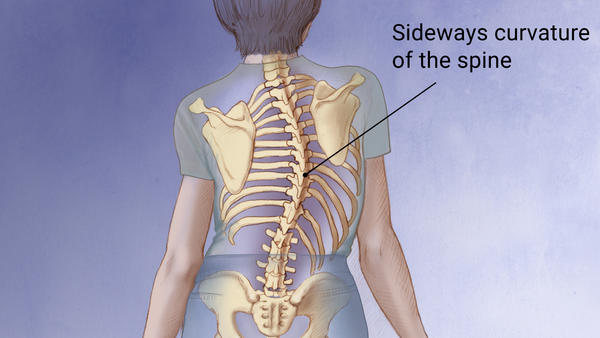
Scoliosis
Short Answer
Definition
Lateral curving of the spinal column
Causes
congenital
idiopathic
damage to the paraspinal muscles as in poliomyelitis (PPRP)
Compression fractures of the vertebral bodies
Osteoporosis
Features
pt inspected standing erect and while stooping
Shoulders are not level
An asymmetric waist line
prominent scapula, accentuated by bending forward
Eldery patients - loss of height due to compression fractures of the vertebrae
Symptoms & Signs
Back ache
Hypoventilation - compromised pulmonary function
Cardiac tamponade
Constipation due to tightened organs from curvature
Pain in back, shoulders, and neck and buttock pain nearest bottom of the back
Limited mobility
Painful menstruation (dysmenorrhea) because of a secondary pelvic tilt
The signs of scoliosis can include:
Uneven musculature on one side of the spine
Rib prominence or a prominent shoulder blade, caused by rotation of the rib cage in thoracic scoliosis
Uneven hips, arms or leg lengths
Slow nerve action
Heart and lung problems in severe cases
Calcium deposits (ectopic calcification) in the cartilage endplate and sometimes in the disc itself
Management
Medical : pain relief with analgesics
Bracing, use of corsets to decrease the progression
Surgery : spinal fusion