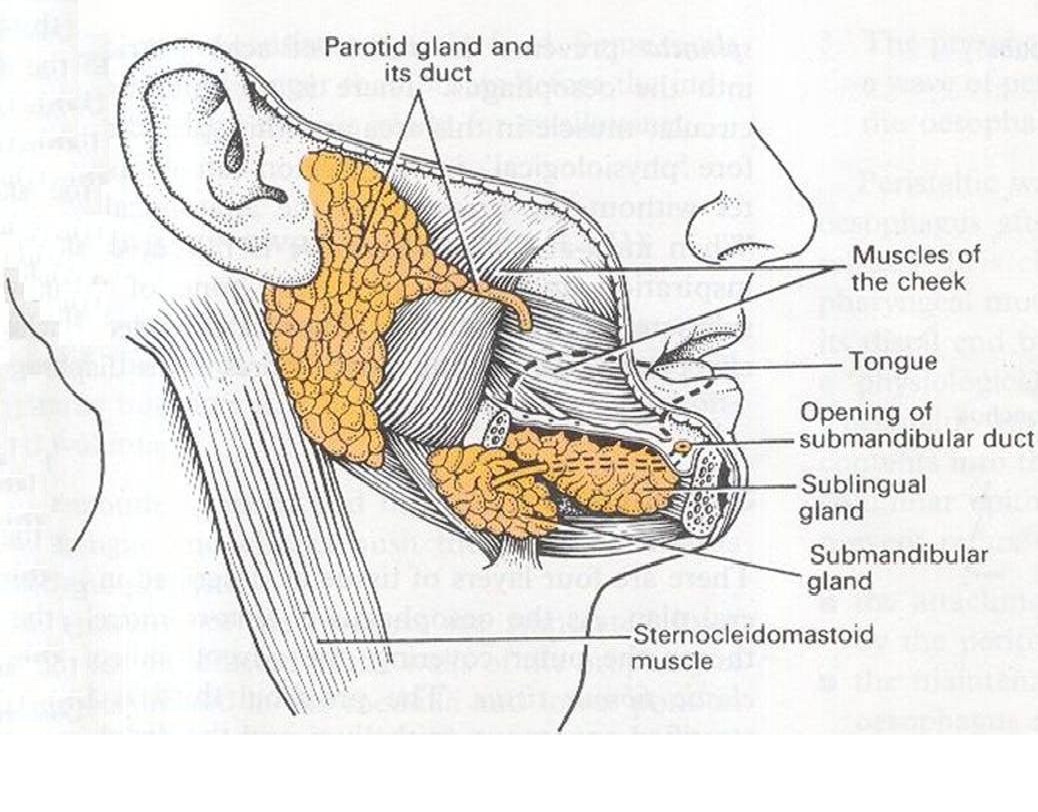
The Salivary Glands
Definition
Salivary glands are structures that produce saliva and pour it into the mouth for the purpose of digestion and moisturisation of the mouth.
Situation
Three major glands :
o Parotid gland is situated on the cheeks just below the ear lobules over the angle of the jaw.
o Submandibular glands - one on either side - under the angle of mandible.
o Sublingual glands one on either side of the frenum of the tongue in the floor of the mouth
Parotid gland :
o Has a superficial lobe and
o A deep lobe
o Separated by faciovenous plane
o Drains into the mouth by an opening situated at the level of the upper second molar tooth
o The duct is called Stensen's duct
Submandibular gland:
o Superficial lobe
o Deep lobe
o Separated by hyoglossus muscle of the floor of the mouth.
o Drains into the mouth by openings situated on either side of the frenum of the tongue.
o The draining duct is called Wharton's duct.
Sublingual glands
o Are situated in the anterior part of the floor of the mouth.
o Open into the floor of the mouth through several small openings.
Innervation
parotid gland receives its parasympathetic input from the glossopharyngeal nerve via the otic ganglion
Submandibular and sublingual glands receive their parasympathetic input from the facial nerve via the submandibular ganglion.
o Sympathetic innervation of the salivary glands come from superior cervical ganglion.
Applied Anatomy
o Parotid gland : mumps viral parotitis, mixed parotid tumour (pleomorphic adenoma)
o Submandibular gland : salivary stones - block the wharton's duct swelling of the glands while eating due to accumulation of saliva.