Ductus Arteriosus / Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Definition & Functioning
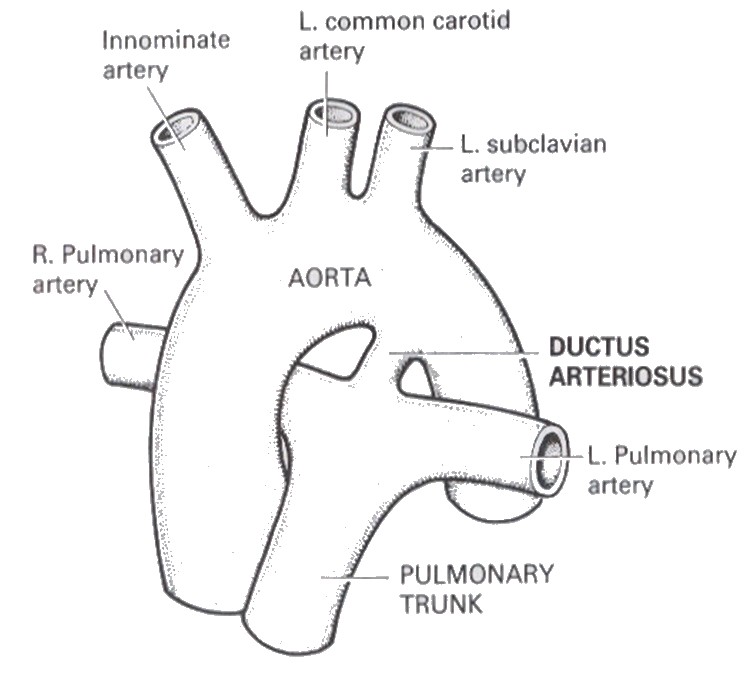
Normal fetal structure - connecting vessel between the left pulmonary artery and the descending thoracic aorta
Normal Physiology
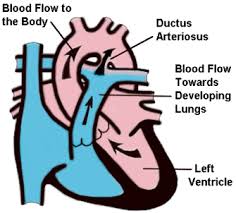
It allows most of the blood from the right ventricle to bypass the fetus's fluid-filled non-functioning lungs -
Shunts blood from the left pulmonary artery to the aorta
Only 5 to 10% of the pulmonary arterial blood reaches the lung
Prostaglandins produced by the placenta and the ductus keep the ductus open
Exposure to high levels of oxygen and the removal of placenta causes it to close within 24 hours
Functional closure usually occurs in the first 15 hours of life,
True anatomic closure takes several weeks by fibrous proliferation of the intima and is complete in 2-3 weeks.
Patency after 3 months is considered abnormal.
If it does not close it is called patent ductus arteriosus
Pathophysiology
The flow is similar to the septal defects (ASD, VSD, Fallot's Tetralogy) but the shunting occurs ouside the heart
Failure of prostaglandin metabolism may keeep the ductus patent
Expanded lungs fail to metabolize the prostaglandins
Pulmonary congestion leads to decreased compliance
Other causes of PDA : preterm birth, Congenital rubella syndrome, Chromosomal abnormalities
Clinical Features
Early symptoms are uncommon
Dyspnoea
Poor weight gain
Tachycardia
Machinary mumur
Cardiomegaly
Left subclavicular thrill
Bounding pulse
Widened pulse pressure
Differential cynosis (cyanosis of the lower extremities but not the upper body)
Features of Congestive Cardiac Failure
Complications
Failure of the DA to close after birth results in :-
patent ductus arteriosus
a left-to-right shunt.
Pulmonary hypertension
Congestive heart failure
Cardiac arrhythmias.
Pulmonary vascular obstructive disease (PVOD)
An anatomic marker : recurrent laryngeal nerve, which passes under the ductus. It is the most commonly injured anatomic structure in ductal ligation. .
Investigations
Echocardiography
ECG
X-Ray chest
Prevention
Indomethacin on the first day of life to all preterm infants
Treatment
Surgical : PDA ligation, intravascular coils or plugs, nitinol wire, percutaneous placement of platinum coil
Medical : NSAIDs
Prognosis
Untreated → Eisenmenger's syndrome (cyanotic heart disease)
Pulmonary hypertension my need a heart and / or lung transplant
.