Congestive Cardiac Failure
Definition
Congestive Cardiac Failure simply known as heart failure is a clinical syndrome caused by the inability of the heart to pump the blood to meet the needs of the body tissues
Invoves the myocardium
Due to systolic dysfunction (contractile function) or due to diastolic dysfunction (filling function)
Often progressive
Causes
Coronary artery disease atherosclerosis
Ischemia
Cardiomyopathy
Systemic or pulmonary hypertension
Pathophysiology
When heart failure occurs the body activates neurohormonal compensatory mechanisms
Systolic HR → decreased blood volume ejected from the ventricle
Sympathetic nervous system is stimulated - release of epinephrine and norepinephrin
Decrease in renal perfusion → release of renin → angiotensin II by ACE → constriction of blood vessels → aldosterone release → sodium and fluid retention
Contractility of the heart muscle reduces as the workload increases
Compensation occurs, muscle thickness increases
Classification
Left sided
Right sided
Left sided Heart Failure
Left ventricle fails to pump adequately
Clinical Features
Dyspnoea on exertion
Cough - initially dry and non productive
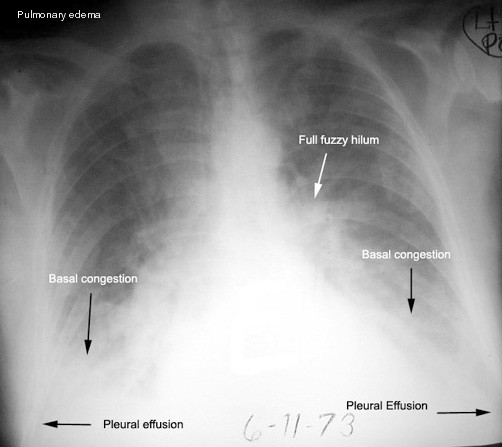
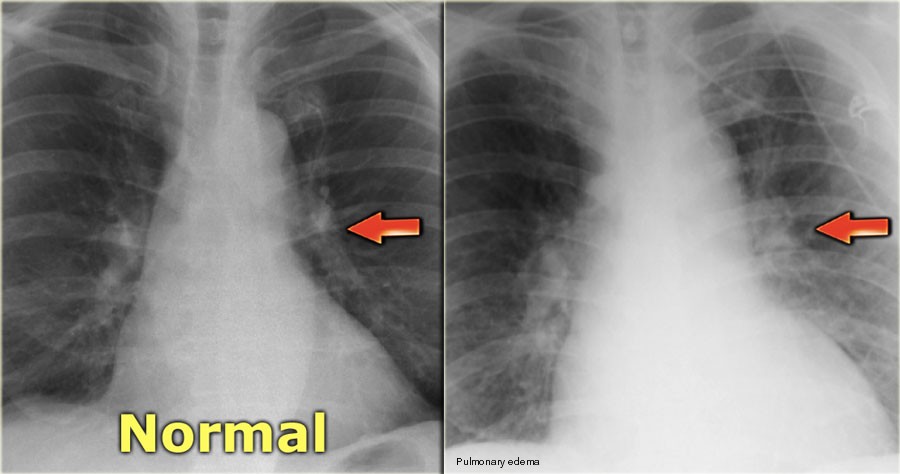
Pulmonary congestion with basal crepitations
Low Oxygen saturation levels
Right sided Heart Failure
Right ventricle fails to pump adequately
Clinical Features
JVP raised
Enlarged Liver due to venous engorgement
Ascites
Gastrointestinal distress
Loss of appetite
Pedal edema
Complications
Hypokalemia - due to repeated diuresis treatment
Hyperkalemia - due to ACE inhibitors/spironolactone
Hyponatremia leading to disorientation, fatigue, apprehension, weakness and muscle cramps
Dehydration and hypotension due to volume depletion
Investigations
ECG
Chest X-ray
Sonograms - Echocardiography
Heart scan (multigated acuisition)
Exercise or pharmacological stress myocardial perfusion (e.g. Persantine or Thallium scan
Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
Cardiac catheterization
Liver enzymes
Digoxin and other cardiac drug levels
Bleeding and clotting times
Electrolytes
Pulse oximetry
Arterial blood gases (ABGs)
BUN/creatinine
Serum albumin/transferrin
CBC
ESR
Thyroid studies
Goals of Treatment
Relieve symptoms
Improve functional status and quality of life
Extend survival
Pharmacological Therapy
ACE inhibitors slow progression, improve exercise tolerance, promote vasodilatation and diuresis, decreases afterload and preload
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers
Block conversion of angiotensinI
cause decreased blood pressure
Decrease vascular resistance
Improve cardiac output
Beta blockers
Reduce the adverse effects on the sympathetic system
Diuretics
Excess extracellular fluid removed
Calcium Channel Blockers
Vasodilatation
Decrease peripheral resistance
Nutritional Therapy
Sodium restriction 2-3 g/day
Additional Therapy
O2
Cardiac resynchronization therapy
Ultrafiltration
Cardiac transplant
Nursing Management
Nursing assessment : elicit signs and symptoms, sleep patterns, patient's understanding of HF
Physical Examination : auscultate lungs, heart, JVP, Sensorium, edema, hepatojugular reflux, urinary output, daily weight
Nursing Diagnosis : Activity intolerance, escess fluid volume, anxiety, powerlessness, ineffective therapeutic management due to lack of knowledge
Planning & Goals
Plan promotion of physical activities, reduction of fatigue, relieve fluid overload, decrease anxiety, encouraging expression of feelings, teaching self-care
Nursing Interventions :
Total 30 mts of physical activity encouraged
Manage fluid volume
Control anxiety
Minimise powerlessness by making the patient to verbalize and encourage decision making
Nursing priorities
Improve myocardial contractility
Reduce fluid volume overload
Prevent complications
Teach
Evaluation
To know outcomes
Measure activity tolerance
assess the maintenance of fluid balance
Lood for reduction of anxiety
Look for decision making
Watch self-care
Discaharge and home care
Pateint educated
Teach the family
Discharge Goals
Adequate cardiac compensation
Complications prevented
Optimum functional capacity
Therapeutic regimen to be understood
Needs after discharge looked after
Proper documentation