Anatomy of the Breast
Definition
Both sexes have breasts : Male breast, Female Breast
Breast of an adult woman is a milk producing gland
Attached to the front of the chest wall on either side of the sternum by ligaments
Sitting on the pectoral muscles
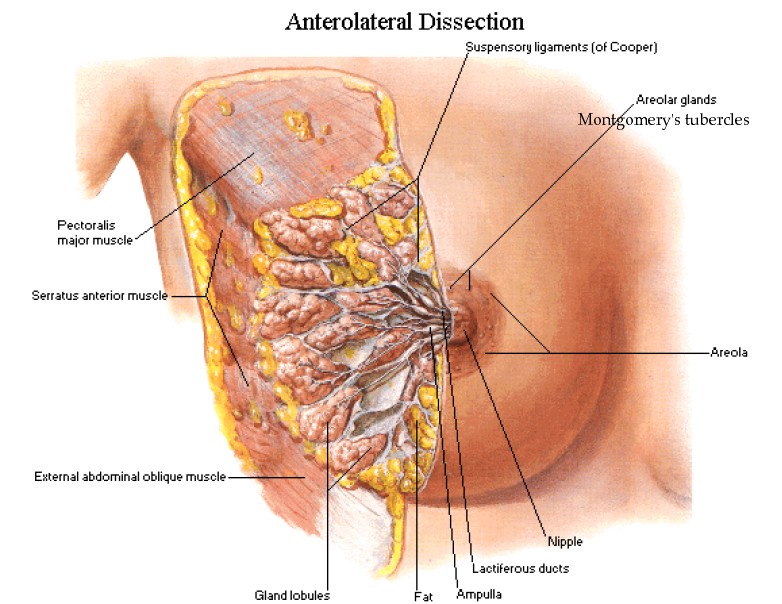
Attached to the chest wall by fibrou ligaments called Cooper's ligaments
Structure
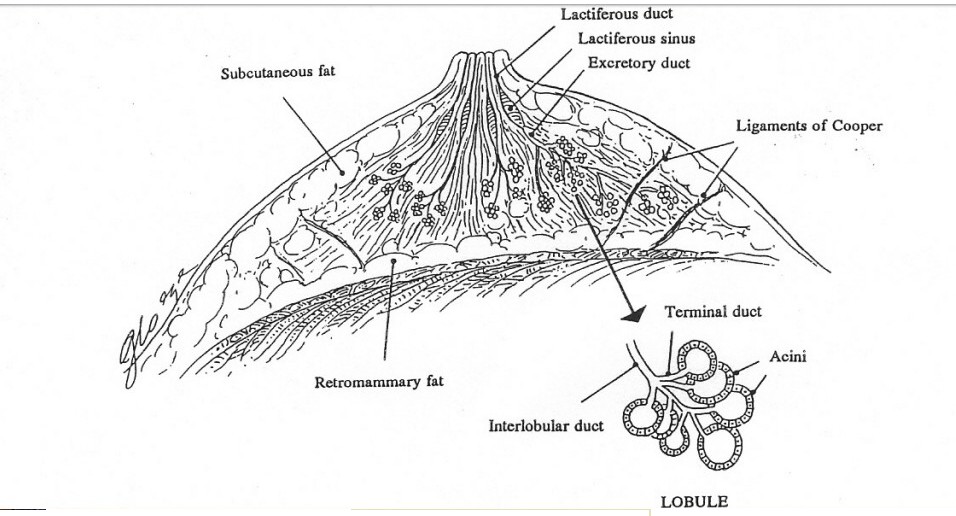
Glands
Fat and fibrous tissues surrounding the glands, the lobules of the glands and ducts.
Glands contain acini
Breast as a whole is soft in consistency
Nipple
Hair follicles around the nipple - hair on the breast
Areola : pink or brown or black circle surrounding the nipple
Nipple and areola contain specialized muscle fibers that respond to stimulation to make the nipple erect
Montgomery's glands - prominent tubercles on the areola - they are modified sweat glands - lubricate the areola
skin
Axillary tail of Spencer - extension of the breast gland into the axilla
Inframammary fold
The margins of the pectoralis manor muscle
Internal Anatomy
Fascial layers
Retromammary space
Fibrous tissue
Glandular tissues/lobes
Lobules
Terminal ductal lobular unit
Adipose tissues
Cooper's ligaments - attach the breast to the chest wall and support it
Pectoral muscle
Circulary system
Lymphatic channels
Histology
Cellular components are Glandular epithelial cells, myoepithelial cells, and the basement membrane
Glandular tissues house the lobules (milk producing glands at the ends of the lobules) and the ducts
Toward the nipple, each duct widens to form a sac ( ampulla)
During lactation, the bulbs on the ends of the lobules produce milk
Transferred through the ducts to the nipple
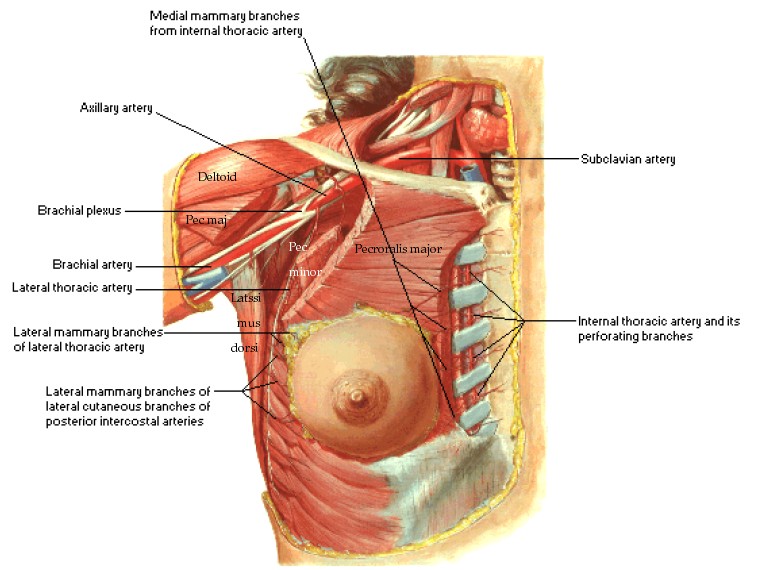
Blood Supply
Axillary artery
Internal mammary artery
Perforating branch of internal thoracic vein
Perforating branch of posterior intercostal vein
tributaries of axillary vein
Nerve Supply
Sympathetic nerves reach via 2nd to 6th intercostal nerves
Overlying skin supplied by anterior and lateral branches of the 4th 5th 6th intercostal nerves
Lymphatic Drainage
6 groups
Axillary vein group (lateral)
External mammary group ( anterior or pectoral) along lower border of pectoralis minor and in relation with lateral thoracic vessels
Scapular group (posterior or subscapular) along subscapular vessels
Central group
Apical/subclavicular
Interpectoral (rotters node)
Levels of Lymphatic Drainage
Level I
Lymph node located lateral to pectoralis minor (lateral axillary, external mammary, subscapular)
Level II
deep to pectoralis minor (central and interpectoral )
Level III
Medial to or above pectoralis minor (subclavicular)
Development
Begins to develop in the 6th week of fetal life
Along a line from the axilla to the groin (milk ridge)
At 9th week the line regresses to the chest area
Applied Anatomy
From the milk ridge - supernumerary nipples - axillary breast (supernumerary breast)
Cancer breast - metastasis to lymph node - infiltration into the lymphatic vessels