Kidney and other Urinary Organs
Name the urinary organs. describe the location, features, relations and blood supply of kidney. (15)
Urinary organs
Kidneys - one on either side - loin
In each kidney - collecting system - Calices and Pelvis
Ureters - one on either side - coursing along the tips of the transvers processes of the lumbar vertebrae
Urinary - one in the midline in the pelvis
Prostate - genital/urinary organ - contains prostatic urethra
Urethra - male & female
Urethral meatus - male & female
Kidney
Location
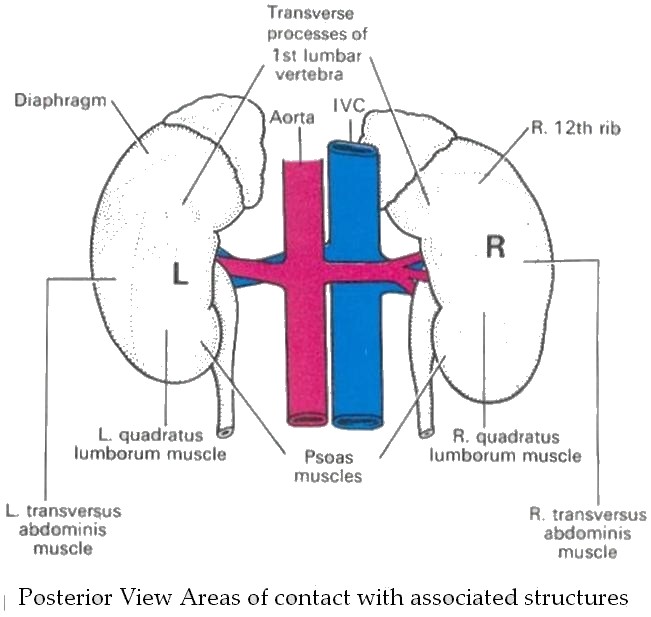
Kidneys lie on the posterior abdominal wall,
One on each side of the vertebral column
Behind the peritoneum
Below the diaphragm
D12 to L3
Right kidney slightly lower
Features
Bean shaped
11cm x 6cm x 3 cm
150 gms
Embedded in a mass of fat
The kidney and the fat enclosed in the renal fascia
Relations
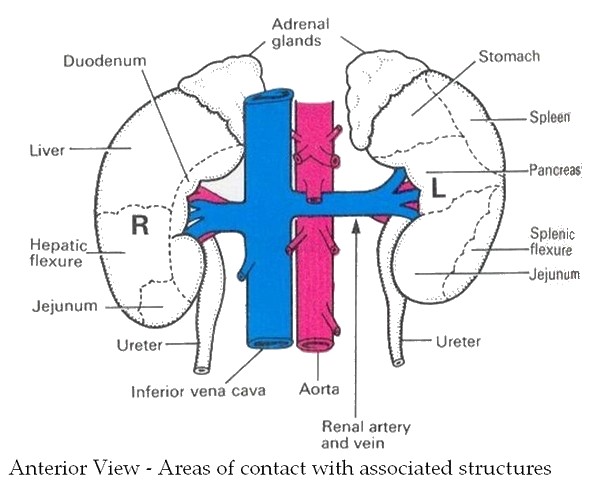
Right Kidney :
Superiorly : adrenal gland
Anteriorly : the right lobe of liver, the duodenum, hepatic flexure of colon
Posteriorly: the diaphragm, muscles of the posterior abdominal wall
Left Kidney :
Superiorly : adrenal gland
Anteriorly : spleen, stomach, pancreas, jejunum and splenic flexure of the colon
Posteriorly : the diaphragm and the muscles of the posterior abdominal wall
Structure of the kidney
Three areas of tissue
A fibrous capsule
The cortex - nephrons
The medulla - pyramids - renal papillae - calices (collecting system)
microscospic structure - Bowman's capsule - glomerulus - afferent arteriole - efferent arteriole - the collecting tubule in three parts : - the proximal convoluted tubule, the loop of Henle, the distal convoluted tubule.
Blood supply of the kidney
The right and left renal arteries - they arise from abdominal aorta.
Venous drainage by right and left renal veins which empty into the inferior vena cava.
Applied anatomy
The kidneys develop in the pelvis and then ascend to the present position in the lumbar region. Failure to ascend → ectopic kidney = pelvic kidney