Psoriasis
Definition
Psoriasis is a chronic noninfectious inflmmatory disease of the skin
Pathophysiology
Epidermal cells produced in excess and fast; the cells in the basal layer divide too quickly having no time for maturation.
Incidence
One of the most common diseases of the skin.
Affects 2 % of the population
15 - 50 yrs
Etiology
Primary cause is unknown
Immune-mediated- not contagious.
A combination of specific genetic makeup and environmental stimuli trigger the onset.
Periods of emotional stress, anxiety, trauma, infections, seasonal & hormonal changes aggravate.
Clinical Manifestations
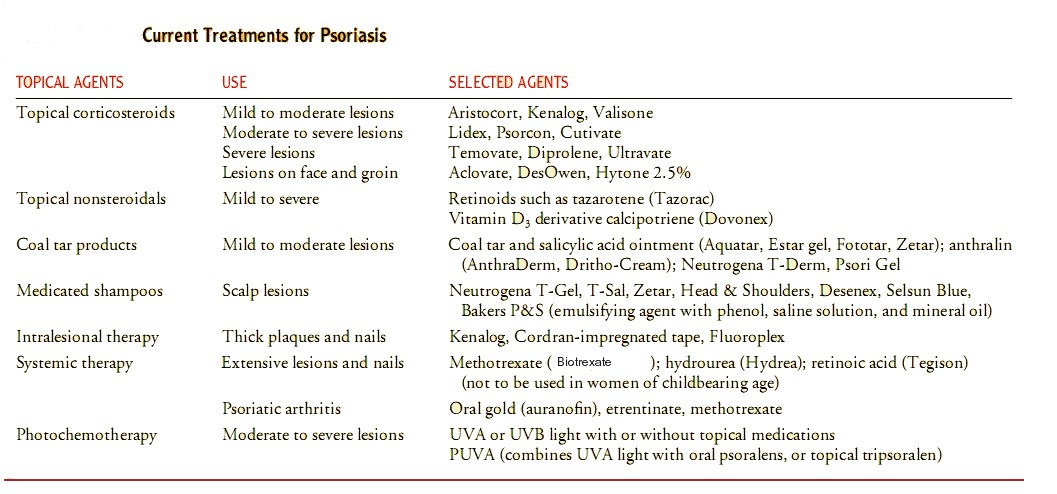
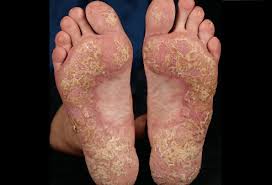
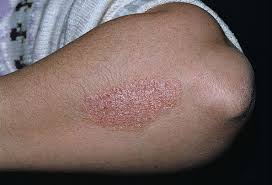
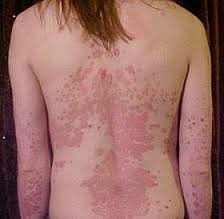
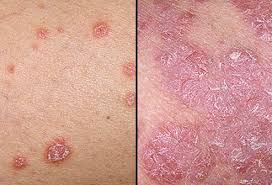
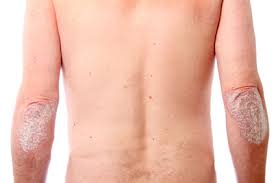
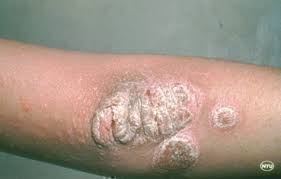
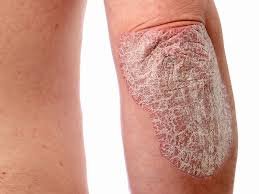
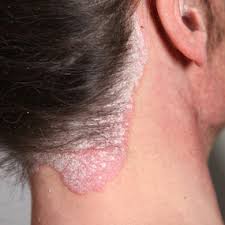
It commonly causes red scaly patches on the skin called psoriatic plaques
Silvery-white appearance.
Plaques on the skin of the elbows and knees, the scalp and genitals.
Itching +
Chronic, recurring
Fingernails and toenails may be involvede
Inflammation of the joints - psoriatic arthritis.
Types of psoariasis
Plaque psoriasis (psoriasis vulgaris) : Most common form
Flexural psoriasis (inverse psoriasis) : Smooth inflamed patches of skin. In skin folds, particularly around the genitals, between the thigh and groin, the armpits, under the breasts aggravated by friction and sweat.
Guttate psoriasis : Numerous small oval (teardrop-shaped) spots. Over trunk, limbs, and scalp.Associated with streptococcal throat infection.
Pustular psoriasis : Filled with non-infectious pus (pustules). Surrounding red and tender.
Nail psoriasis : Changes the appearance of finger and toe nails. Discolouration, Pitting of the nails, lines going across the nails, Thickening of the skin under the nail, Loosening, crumbling of the nail.
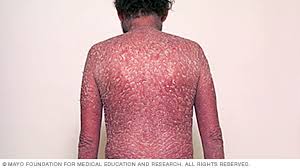
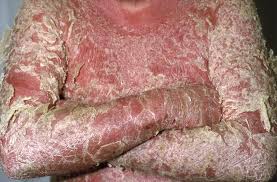
Erythrodermic psoriasis : Widespread inflammation and exfoliation of the skin over most of the body surface. Accompanied by severe itching, swelling and pain. Following the abrupt withdrawal of systemic treatment. May be fatal