The Prostate
Definition
The prostate gland is part of the male reproductive and urinary systems.
Location
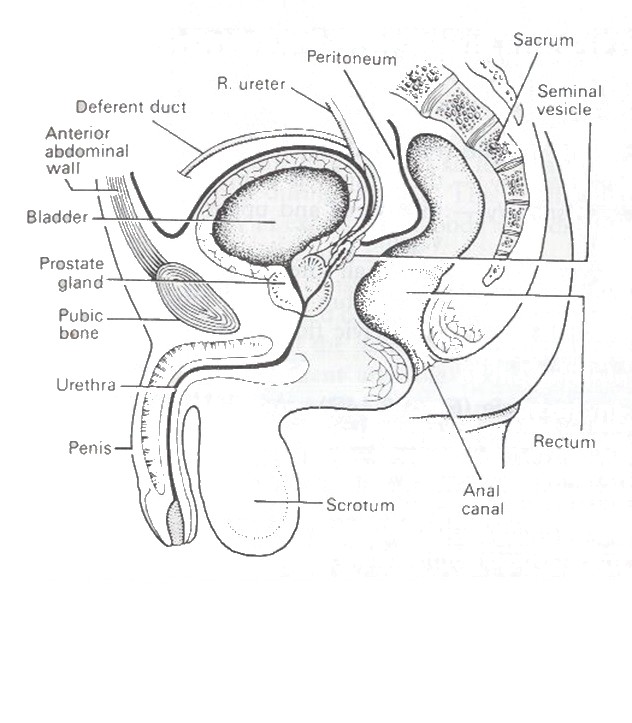
The prostate surrounds the base (or neck) of the bladder
Structure
The prostate is oval shaped with a rounded tip.
4 cm wide and 3 cm thick. The actual size of the prostate varies from man to man.
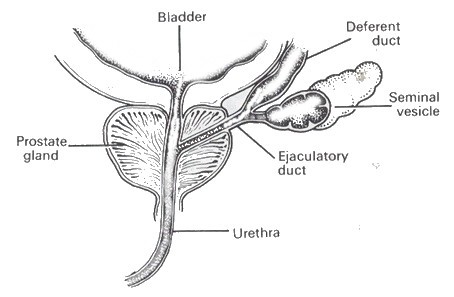
It has 2 lobes that surround the urethra.
The urethra carries urine from the bladder, through the prostate, and out the penis.
It is covered in a layer of connective tissue called the prostatic capsule.
It is made up of different types of cells:
Gland cells that produce the fluid portion of semen
Muscle cells that control urine flow and ejaculation
Fibrous cells that provide the supportive structure of the gland
Structures around the prostate :
seminal vesicles – produce semen and are found on both sides of the prostate.
vas deferens – carry sperm from the testicles to the seminal vesicles.
nerve bundles – control bladder and erectile function and are found on both sides of the prostate.
muscles – control urination.
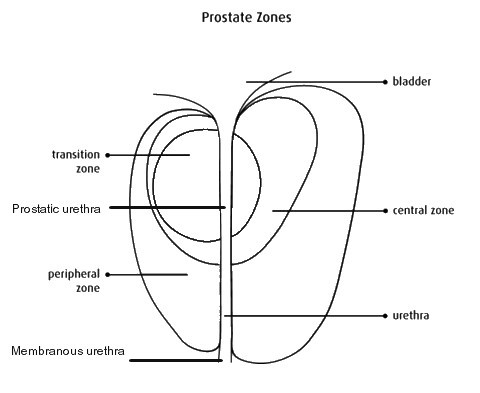
Zones of the prostate
The prostate gland is divided into 3 zones:
peripheral zone
transition zone
central zone
Peripheral zone
closest to the rectum. It can easily be felt during a digital rectal examination - the largest zone of the prostate gland.
The majority of prostate tumours (approximately 75%) are found in the peripheral zone.
Transition zone
The area of the prostate that surrounds the urethra as it passes through the prostate.
This zone makes up about 20% of the prostate gland until the age of 40.
As men age, the transition zone begins to enlarge, until it becomes the largest area of the prostate.
Central zone
It is in front of the transition zone.
Function
Produces the fluid portion of semen.
The fluid maintains and nourishes the sperm. This fluid is made continuously. The excess passes from the body in the urine. When a man is sexually aroused, the prostate produces larger amounts of this fluid. It then mixes with sperm and is ejaculated as semen.
The prostate also plays a part in controlling the flow of urine.
The muscle fibres of the prostate are wrapped around the urethra and are under involuntary nervous system control. These fibres contract to slow and stop the flow of urine.