Adrenal Glands
Definition
Also known as suprarenal glands
Triangle-shaped endocrine glands
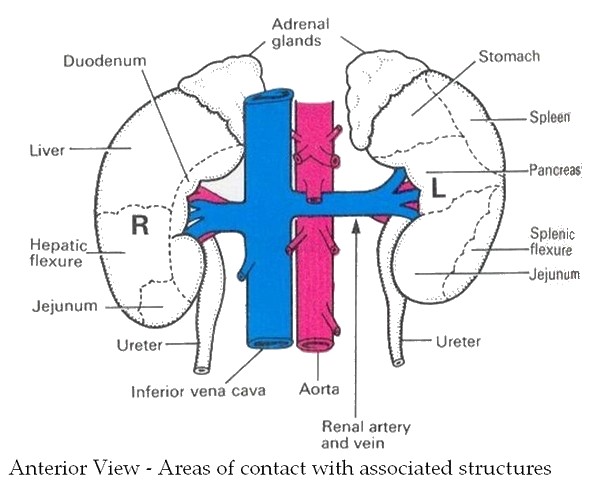
Situated on top of the kidneys
At the level of the D12
Regulating the stress response thru the synthesis of corticosteroids and catecholamines, including cortisol and adrenaline.
The adrenals receive regulatory input from the nervous system:
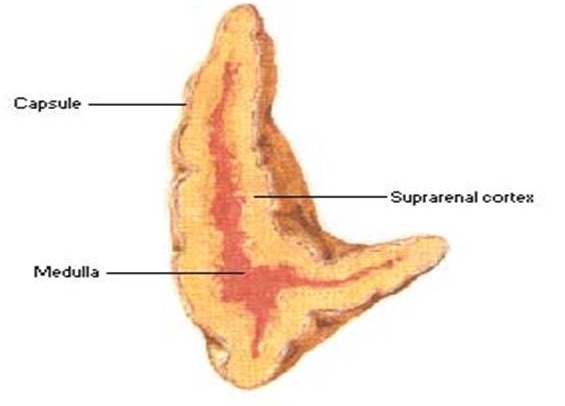
Adrenal medulla
It is the central core of the adrenal gland, surrounded by the adrenal cortex.
Consists of chromaffin cells
Synthesises adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine).
Responsible for the fight-or-flight response initiated by the sympathetic nervous system.
Can be considered specialized ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system
Also secretes dopamine
Adrenal cortex
Synthesises corticosteroid hormones from cholesterol.
Produce androgens : testosterone
Aldosterone regulates water and electrolyte concentrations.
Regulated by neuroendocrine hormones secreted by the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, as well as by the renin-angiotensin system.
Blood supply
The superior suprarenal artery- from inferior phrenic
The middle suprarenal artery - from abdominal aorta
The inferior suprarenal artery - from renal artery
Venous drainage of the adrenal glands is achieved via the suprarenal veins:
The right suprarenal vein drains into the inferior vena cava
The left suprarenal vein drains into the left renal vein or the left inferior phrenic vein.